Discover the key differences between AC motors and DC motors, their unique advantages, and how to choose the right one for your application.
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to powering modern devices and machinery, the choice between AC motors and DC motors is a critical decision that can impact performance, efficiency, and cost. Whether you’re designing a smart home device, a robotic system, or a medical care tool, understanding the differences between these two motor types is essential.
AC motors (Alternating Current motors) and DC motors (Direct Current motors) each have unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications. While AC motors are known for their durability and ability to handle high-power tasks, DC motors excel in applications requiring precise speed control and compact designs.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the key differences between AC motors and DC motors, explore their advantages, and help you determine which motor type is best suited for your needs. By the end, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how these motors work and where they shine in industries like smart home technology, robotics, and more.
Let’s get started by breaking down what AC and DC motors are and how they operate.
What Are AC Motors and DC Motors?
To understand the differences between AC motors and DC motors, it’s important to first grasp how each type operates and what makes them unique. While both are used to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, they do so in fundamentally different ways.
What is an AC Motor?
An AC motor (Alternating Current motor) runs on alternating current, which means the direction of the electrical flow reverses periodically. This type of motor is widely used in applications where high power and consistent performance are required. AC motors are known for their simplicity, reliability, and ability to operate at high speeds without the need for frequent maintenance.
Common examples of AC motors include induction motors and synchronous motors. These motors are often found in industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and household appliances like washing machines and fans. Their ability to handle heavy loads and operate efficiently over long periods makes them a popular choice for many applications.
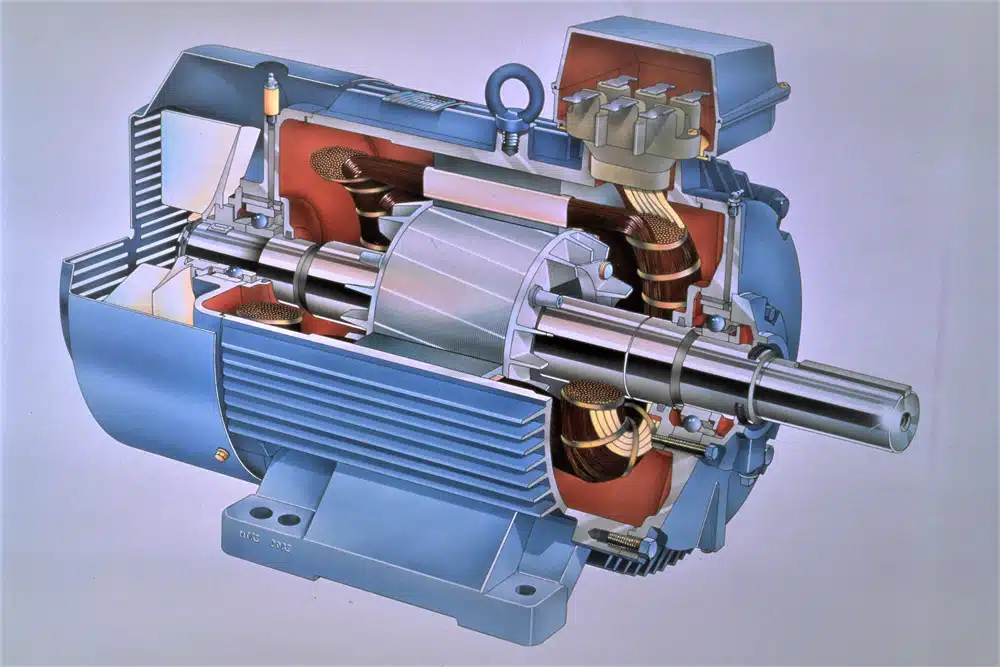
What is a DC Motor?
On the other hand, a DC motor (Direct Current motor) operates on direct current, where the electrical flow moves in a single direction. DC motors are prized for their precise speed control, compact size, and ease of use. They are particularly well-suited for applications that require variable speeds or frequent start-stop cycles.
DC motors come in various types, including brushed and brushless motors. Brushed DC motors are simpler and more cost-effective, while brushless DC motors offer higher efficiency and longer lifespans. These motors are commonly used in robotics, electric vehicles, and small devices like vending machines and medical equipment.
By understanding the basic principles of AC and DC motors, you can start to see why each type is better suited for certain tasks. In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into the key differences between AC motors and DC motors to help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.

Key Differences Between AC Motors and DC Motors
Now that we’ve covered the basics of AC motors and DC motors, let’s dive into the key differences that set them apart. Understanding these distinctions will help you determine which motor type is better suited for your specific application, whether it’s for smart home devices, robotics, or industrial machinery.
1. Power Source and Voltage Requirements
One of the most fundamental differences between AC and DC motors lies in their power sources. AC motors are designed to run on alternating current, which is the standard form of electricity supplied by power grids. This makes them ideal for applications where direct access to mains power is available, such as in household appliances or large industrial equipment.
On the other hand, DC motors operate on direct current, which is often supplied by batteries or rectifiers. This makes them a better fit for portable devices, electric vehicles, and applications where consistent voltage is required. For example, many smart home devices and robotics systems rely on DC motors because they can be powered by small batteries or low-voltage power supplies.
2. Speed Control and Efficiency
When it comes to speed control, DC motors have a clear advantage. They offer precise and smooth speed regulation, making them ideal for applications like robotics, conveyor systems, and medical devices where variable speeds are critical. Additionally, DC motors tend to be more efficient at lower speeds, which can lead to energy savings in certain use cases.
AC motors, however, are generally more efficient at higher speeds and are better suited for applications that require constant speed operation, such as fans, pumps, and compressors. While AC motors can be equipped with variable frequency drives (VFDs) to adjust speed, this adds complexity and cost to the system.
3. Maintenance and Lifespan
Maintenance requirements are another area where AC and DC motors differ significantly. AC motors are known for their durability and low maintenance needs, thanks to their simple design and lack of brushes. This makes them a reliable choice for heavy-duty applications where downtime must be minimized.
In contrast, DC motors, especially brushed types, require more frequent maintenance due to brush wear. However, brushless DC motors have emerged as a popular alternative, offering longer lifespans and reduced maintenance needs while retaining the benefits of precise speed control.
4. Size and Weight
For applications where space is at a premium, DC motors often have the upper hand. They are typically more compact and lightweight than AC motors, making them ideal for small devices like vending machines, sanitary dispensers, and portable medical equipment.
AC motors, while bulkier, are better suited for applications where size and weight are less of a concern, such as in industrial machinery or HVAC systems.
By understanding these key differences, you can start to see why certain applications favor one motor type over the other. In the next section, we’ll explore the advantages of AC motors in greater detail to help you identify where they excel.
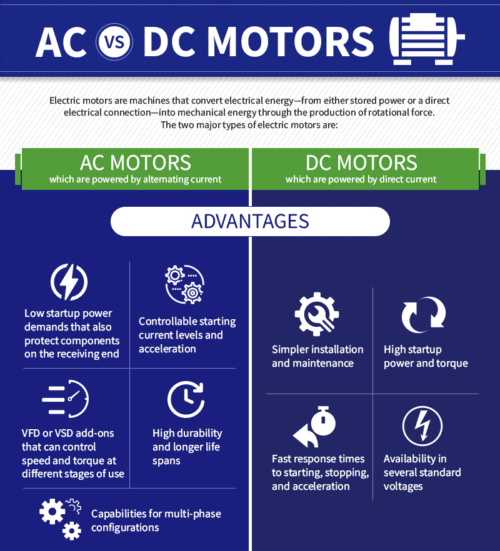
Advantages of AC Motors
When it comes to reliability and performance in demanding environments, AC motors have a lot to offer. Their design and functionality make them a go-to choice for many industrial and commercial applications. Let’s take a closer look at the key advantages of AC motors and why they might be the right fit for your needs.
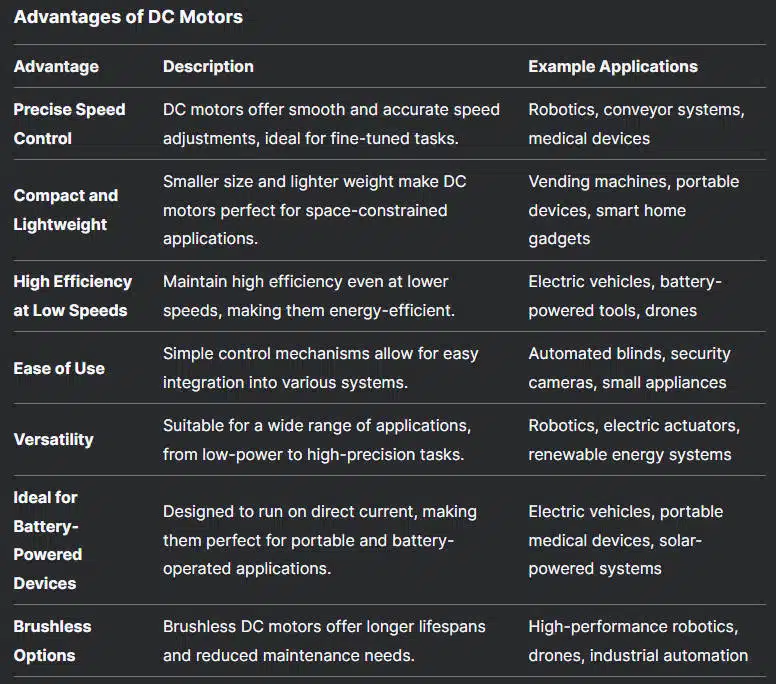
1. Durability and Longevity
One of the standout features of AC motors is their durability. Thanks to their simple construction and lack of brushes, AC motors are less prone to wear and tear compared to their DC counterparts. This makes them ideal for applications that require continuous operation over long periods, such as in HVAC systems, industrial pumps, and conveyor belts.
For example, in smart home devices like automated gates or garage door openers, AC motors provide reliable performance with minimal maintenance. Their ability to handle heavy loads without frequent breakdowns ensures a longer lifespan, reducing the total cost of ownership over time.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Another significant advantage of AC motors is their cost-effectiveness. Because they are widely used in industrial and household applications, they benefit from economies of scale, making them more affordable to produce and purchase. Additionally, their low maintenance requirements translate to lower operational costs over their lifespan.
In applications like electric valves or sanitary dispensers, where consistent performance is critical, AC motors offer a cost-efficient solution without compromising on reliability. This makes them a popular choice for manufacturers looking to balance performance and budget.
3. High Power and Efficiency at Constant Speeds
AC motors excel in applications that require high power output and consistent speed. Their ability to operate efficiently at constant speeds makes them ideal for devices like fans, compressors, and industrial machinery. For instance, in electric meter systems, AC motors ensure accurate and reliable operation over extended periods.
Moreover, AC motors can handle sudden load changes without significant performance drops, making them suitable for environments where operational demands can vary. This robustness is particularly valuable in industries like manufacturing and energy, where downtime can be costly.
4. Compatibility with Mains Power
Since AC motors run on alternating current, they are directly compatible with the standard power supply from electrical grids. This eliminates the need for additional converters or power supplies, simplifying installation and reducing overall system complexity.
In smart home systems, for example, AC motors can be seamlessly integrated into existing electrical setups, making them a convenient choice for homeowners and builders alike.
By leveraging these advantages, AC motors continue to dominate applications where durability, cost-efficiency, and high power output are paramount. In the next section, we’ll shift our focus to the advantages of DC motors and explore where they outperform AC motors.
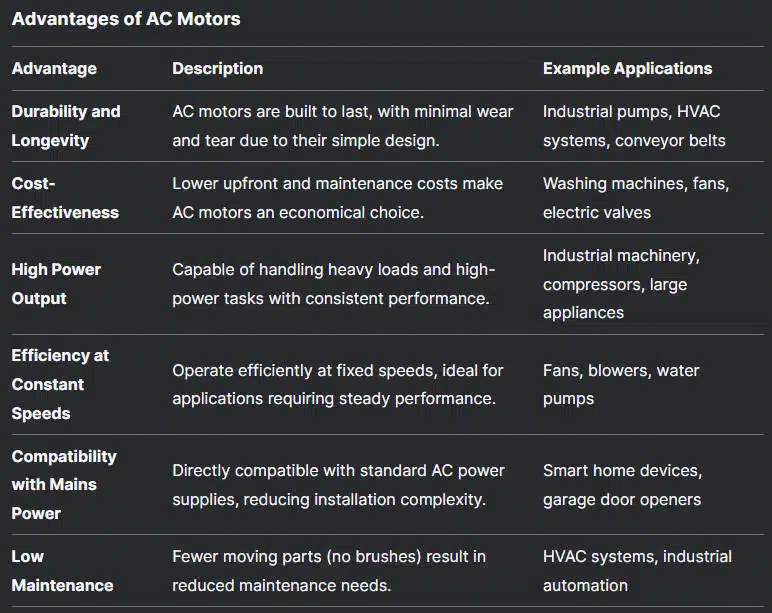
Advantages of DC Motors
While AC motors excel in many areas, DC motors bring their own set of unique advantages to the table. Known for their precision, compact design, and versatility, DC motors are the preferred choice for a wide range of applications, especially those requiring fine-tuned control and portability. Let’s explore the key benefits of DC motors and why they might be the perfect solution for your project.
1. Precise Speed Control
One of the most significant advantages of DC motors is their ability to deliver precise speed control. Unlike AC motors, which typically operate at a fixed speed unless paired with additional equipment like variable frequency drives (VFDs), DC motors can easily adjust their speed with simple changes to the input voltage.
This makes DC motors ideal for applications like robotics, where precise movement and responsiveness are critical. For example, in robotic arms used in manufacturing or medical care, DC motors enable smooth and accurate positioning, ensuring high-quality performance.
2. Compact and Lightweight Design
DC motors are generally more compact and lightweight than AC motors, making them a great fit for applications where space is limited. Their smaller size allows them to be integrated into portable devices, small appliances, and miniaturized systems without compromising performance.
In industries like vending machines and sanitary dispensers, where space optimization is crucial, DC motors provide the necessary power in a compact form factor. This design flexibility also extends to smart home devices, such as automated blinds or small security systems, where aesthetics and size matter.
3. High Efficiency at Low Speeds
Another standout feature of DC motors is their high efficiency at low speeds. While AC motors tend to perform better at constant, high-speed operations, DC motors maintain their efficiency even at lower speeds, making them energy-efficient choices for applications like electric vehicles or battery-powered tools.
For instance, in electric valve systems or medical devices like infusion pumps, DC motors ensure reliable operation while conserving energy, which is especially important in battery-dependent scenarios.
4. Ease of Use and Versatility
DC motors are known for their simplicity and ease of use. They can be easily controlled using basic electronic circuits, making them accessible for a wide range of applications. Additionally, the availability of brushless DC motors has further enhanced their appeal by offering longer lifespans and reduced maintenance needs.
In fields like robotics and automation, where customization and adaptability are key, DC motors provide the versatility needed to meet diverse operational requirements. Their ability to start, stop, and reverse direction quickly also makes them suitable for applications like conveyor systems and electric actuators.
5. Ideal for Battery-Powered Applications
Since DC motors run on direct current, they are perfectly suited for battery-powered devices. This makes them a popular choice for portable electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy systems like solar-powered devices.
For example, in smart home security systems, DC motors power components like camera pan-tilt mechanisms, ensuring reliable performance even when running on backup batteries.
By leveraging these advantages, DC motors continue to play a vital role in industries that demand precision, portability, and energy efficiency. In the next section, we’ll explore the applications of AC and DC motors to help you identify which type aligns best with your specific needs.
Applications of AC Motors and DC Motors
Understanding the strengths of AC motors and DC motors is only half the battle—knowing where each type excels in real-world applications is equally important. Both motor types have carved out their niches across various industries, from smart home technology to medical care. Let’s explore some of the most common applications for each motor type to help you see where they shine.
Where Are AC Motors Used?
AC motors are the workhorses of industries that require high power, durability, and consistent performance. Here are some key areas where AC motors are commonly used:
Smart Home Devices: AC motors power devices like garage door openers, HVAC systems, and washing machines, where reliability and continuous operation are essential.
Industrial Machinery: In manufacturing and production lines, AC motors drive conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors, handling heavy loads with ease.
Electric Valves and Meters: AC motors ensure accurate and reliable operation in utility systems, such as water meters and gas valves.
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems rely on AC motors for fans and blowers, providing efficient climate control.
These applications benefit from the robustness, low maintenance, and cost-effectiveness of AC motors, making them a staple in many industries.
Where Are DC Motors Used?
DC motors, on the other hand, are the go-to choice for applications that demand precision, portability, and energy efficiency. Here are some common uses for DC motors:
Robotics: DC motors are integral to robotic systems, enabling precise movements in robotic arms, drones, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Medical Devices: In medical care, DC motors power equipment like infusion pumps, surgical tools, and diagnostic machines, where accuracy and reliability are critical.
Smart Home Security: DC motors are used in security cameras, automated locks, and alarm systems, providing quiet and efficient operation.
Vending Machines and Sanitary Dispensers: The compact size and precise control of DC motors make them ideal for these devices, ensuring smooth and reliable functionality.
Electric Vehicles: DC motors, especially brushless types, are widely used in electric cars, scooters, and bikes due to their efficiency and ability to run on battery power.
These applications highlight the versatility and adaptability of DC motors, particularly in scenarios where space, precision, and energy efficiency are paramount.
Overlap in Applications
While AC and DC motors each have their preferred domains, there are areas where their applications overlap. For example, both motor types can be found in smart home systems: AC motors might power larger appliances like refrigerators, while DC motors drive smaller devices like smart blinds or security cameras.
Similarly, in industrial automation, AC motors handle heavy machinery, while DC motors are used for precise positioning and control in robotic arms or conveyor systems.
By understanding these applications, you can better appreciate how AC motors and DC motors complement each other in modern technology. In the next section, we’ll provide practical tips on how to choose between AC and DC motors for your specific needs.
How to Choose Between AC Motors and DC Motors
Choosing between AC motors and DC motors can feel overwhelming, especially with the wide range of applications and technical considerations involved. However, by focusing on a few key factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your project’s requirements. Here’s a practical guide to help you determine which motor type is the best fit for your needs.
1. Consider Your Power Source
The first step in choosing a motor is to evaluate your power supply. If your application has direct access to mains power (alternating current), an AC motor might be the more straightforward choice. AC motors are designed to work seamlessly with standard electrical grids, eliminating the need for additional converters or power supplies.
On the other hand, if your device runs on batteries or requires a low-voltage power supply, a DC motor is likely the better option. DC motors are inherently compatible with direct current, making them ideal for portable or battery-powered applications like robotics, electric vehicles, and smart home devices.
2. Evaluate Speed Control Requirements
If your application demands precise speed control, DC motors are the clear winner. Their ability to adjust speed smoothly and accurately makes them perfect for tasks like robotic movements, conveyor systems, and medical devices.
For applications where constant speed is sufficient, such as fans, pumps, or compressors, AC motors are often more efficient and cost-effective. While AC motors can achieve variable speed control with the help of variable frequency drives (VFDs), this adds complexity and cost to the system.
3. Assess Maintenance and Lifespan Needs
Maintenance requirements are another critical factor to consider. AC motors are known for their durability and low maintenance, thanks to their simple design and lack of brushes. This makes them a reliable choice for heavy-duty applications where downtime must be minimized.
In contrast, DC motors, particularly brushed types, require more frequent maintenance due to brush wear. However, brushless DC motors offer a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance needs, making them a viable alternative for applications that demand precision and reliability.
4. Factor in Size and Weight Constraints
For applications where space is limited, DC motors often have the upper hand. Their compact and lightweight design makes them ideal for small devices like vending machines, sanitary dispensers, and portable medical equipment.
If size and weight are less of a concern, AC motors can provide the power and durability needed for larger systems like industrial machinery or HVAC units.
5. Analyze Cost and Efficiency
Finally, consider your budget and energy efficiency requirements. AC motors are generally more cost-effective for high-power applications, thanks to their widespread use and low maintenance needs. They also tend to be more efficient at constant speeds, making them a practical choice for many industrial and commercial applications.
DC motors, while sometimes more expensive upfront, offer energy savings in applications that require variable speeds or operate at lower power levels. Their efficiency at low speeds and precise control capabilities can lead to long-term cost savings in the right scenarios.
Still Unsure? Consult the Experts
If you’re still unsure which motor type is best for your application, don’t hesitate to reach out to a trusted manufacturer like Etonm Motor. With years of experience in producing custom motors for industries like smart home, robotics, and medical care, we can help you find the perfect solution tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Choosing between AC motors and DC motors is a decision that hinges on your specific application needs, from power sources and speed control to maintenance and cost considerations. Both motor types bring unique strengths to the table, making them indispensable in industries like smart home technology, robotics, medical care, and industrial automation.
AC motors stand out for their durability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to handle high-power tasks, making them ideal for applications like HVAC systems, industrial machinery, and household appliances. On the other hand, DC motors excel in scenarios requiring precise speed control, compact design, and energy efficiency, such as robotics, electric vehicles, and portable medical devices.
By understanding the key differences and advantages of each motor type, you can make an informed choice that ensures optimal performance and efficiency for your project. Whether you’re designing a cutting-edge robotic system or upgrading your smart home devices, the right motor can make all the difference.
If you’re still unsure which motor is best suited for your needs, don’t hesitate to reach out to Etonm Motor. As a leading manufacturer of custom motors, including planetary gear motors, worm gear motors, and brushless motors, we’re here to help you find the perfect solution. Contact us today to learn more about our products and how we can support your next project.
Our Micro DC Motor Models
Related Reading
- Why BLDC Motors Are the Future of Electric Vehicles: A Complete Guide
- Brushless DC Motors in Medical Devices: The Ultimate Guide to BLDC Motor Applications
- Top 5 Applications of Brushless DC Motors in Industrial Automation
- BLDC Motor vs Brushed Motor: Which is Better for Your Needs?
- The Ultimate Guide to Brushless DC Motors: Types, Applications, and Benefits
- Introduction of 12V DC Micro Motor Products
- Why Choose 24v Small DC Motors?
- How To Choose A Brushless Gear Motor | Etonm Motor Guide


















