Discover the key differences between BLDC motors and brushed motors, their advantages, disadvantages, and which one suits your specific application needs.
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to powering modern devices—from smart home systems to medical equipment—the choice of motor can make all the difference. Two of the most common options are BLDC motors (Brushless DC motors) and brushed motors, each with its own set of strengths and weaknesses. But how do you decide which one is better for your specific needs?
The debate of BLDC Motor vs Brushed Motor is more relevant than ever, especially as industries like robotics, electric valves, and vending machines demand higher efficiency, durability, and precision. BLDC motors are known for their advanced technology and low maintenance, while brushed motors remain popular for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between these two motor types, explore the advantages of BLDC motors, and highlight the disadvantages of brushed motors. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which motor is the right fit for your application. Let’s dive in!
What is a BLDC Motor?
A BLDC motor (Brushless DC motor) is a modern, high-performance motor that operates without the brushes found in traditional brushed motors. Instead, it uses an electronic controller to manage commutation, which is the process of switching the current in the motor’s windings to keep it running. This design eliminates the physical contact between brushes and commutators, reducing friction and wear.
One of the standout advantages of BLDC motors is their efficiency. Because there’s no energy loss due to brush friction, BLDC motors can convert more electrical energy into mechanical power, making them ideal for applications where energy consumption matters. They’re also known for their durability—since there are no brushes to wear out, these motors have a significantly longer lifespan and require minimal maintenance.
BLDC motors are widely used in industries that demand precision and reliability, such as robotics, smart home devices, and medical equipment. For example, in a robotic arm or an electric valve, the smooth and consistent performance of a BLDC motor ensures accurate control and long-term operation.
In summary, BLDC motors are a smart choice for applications that prioritize efficiency, durability, and low maintenance. But how do they stack up against their brushed counterparts? Let’s explore that next.

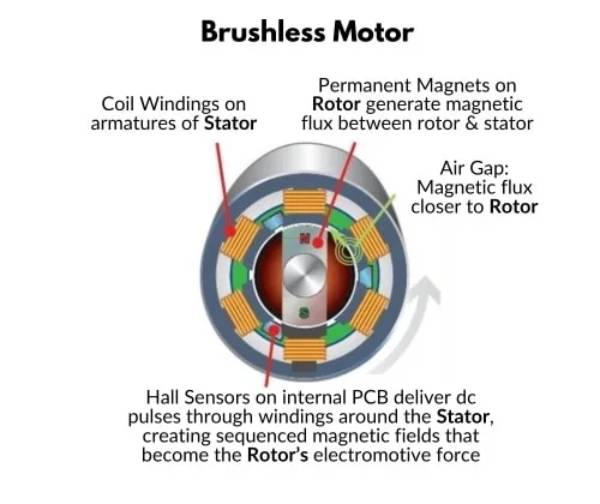
What is a Brushed Motor?
A brushed motor is one of the oldest and most widely used types of electric motors. It operates using a simple yet effective design: brushes made of carbon or graphite make physical contact with a commutator to deliver current to the motor’s windings. This process creates the magnetic fields needed to generate motion.
Brushed motors are known for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They are easy to manufacture and require minimal electronic control, making them a popular choice for low-cost applications. For example, they are often used in small household appliances, basic toys, and other devices where performance demands are modest.
However, brushed motors come with some notable disadvantages. The physical contact between the brushes and commutator leads to friction, which reduces efficiency and generates heat. Over time, the brushes wear out and need to be replaced, increasing maintenance requirements. Additionally, brushed motors tend to have a shorter lifespan compared to BLDC motors, especially in high-speed or high-load applications.
Despite these drawbacks, brushed motors still have their place in certain scenarios. For instance, in cost-sensitive projects or applications where simplicity is more important than performance, brushed motors can be a practical solution.
In the next section, we’ll dive deeper into the key differences between BLDC motors and brushed motors to help you make an informed decision for your specific needs.

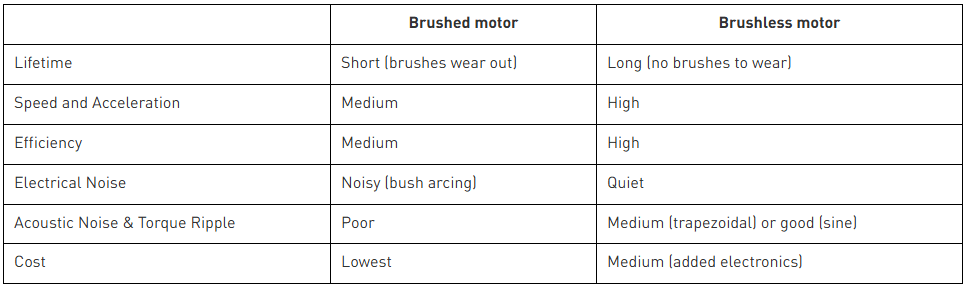
BLDC Motor vs Brushed Motor: Key Differences
When comparing BLDC motors and brushed motors, several key factors come into play. Understanding these differences can help you determine which motor type is better suited for your application. Let’s break it down:
1. Efficiency
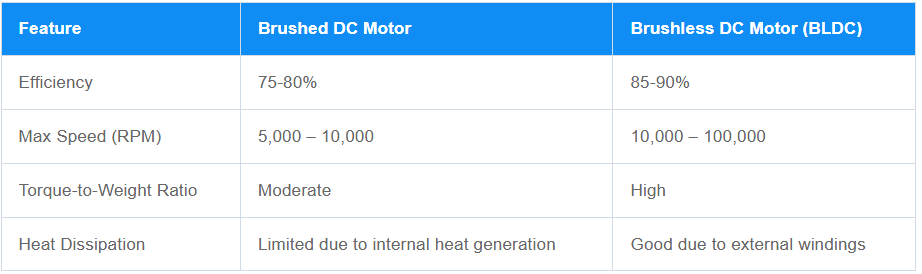
BLDC Motors: These motors are highly efficient because they eliminate the energy loss caused by brush friction. They can convert up to 85-90% of electrical energy into mechanical power, making them ideal for energy-sensitive applications like smart home devices and medical equipment.
Brushed Motors: Due to the constant friction between brushes and the commutator, brushed motors are less efficient, typically converting only 75-80% of electrical energy into mechanical power. This makes them less suitable for applications where energy consumption is a concern.
Efficiency and Performance Difference between BLDC Motors and Brushed Motors
2. Lifespan
BLDC Motors: With no brushes to wear out, BLDC motors have a significantly longer lifespan. They are designed to operate reliably for thousands of hours, even in demanding environments like robotics or industrial automation.
Brushed Motors: The brushes in these motors wear down over time and need regular replacement, leading to a shorter overall lifespan. This makes them less ideal for applications requiring long-term reliability.
3. Maintenance
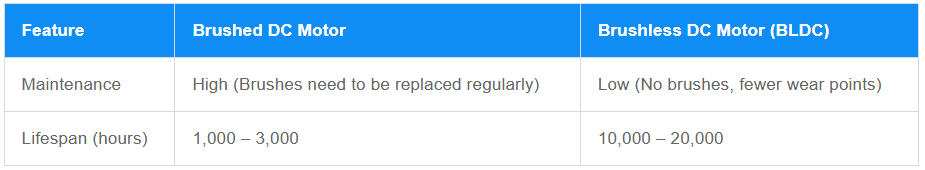
BLDC Motors: These motors are virtually maintenance-free since there are no brushes to replace. This reduces downtime and operational costs, especially in applications like electric valves or vending machines.
Brushed Motors: Regular maintenance is required to replace worn-out brushes and clean the commutator. This can increase long-term costs and inconvenience, particularly in hard-to-access systems.
Maintenance and Lifespan Difference between BLDC Motors and Brushed Motors
4. Noise and Operation
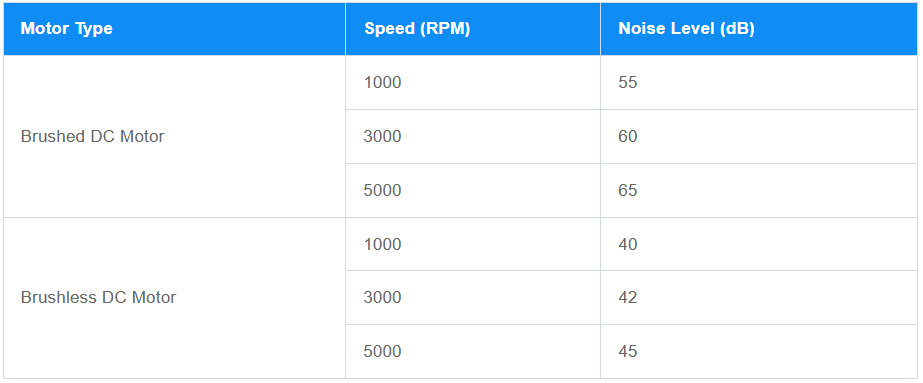
BLDC Motors: They operate more quietly and smoothly because there’s no physical contact between brushes and a commutator. This makes them perfect for applications like medical devices or smart home systems where noise levels matter.
Brushed Motors: The friction between brushes and the commutator generates more noise and vibration, which can be a drawback in noise-sensitive environments.
Noise Difference between BLDC Motors and Brushed Motors
5. Cost
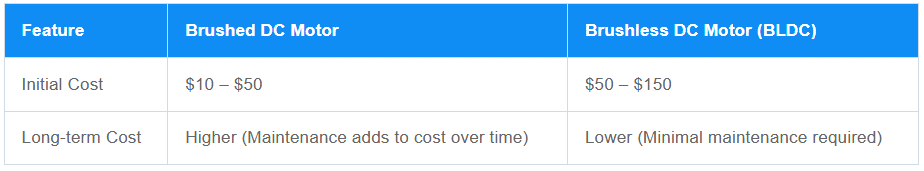
BLDC Motors: While BLDC motors have a higher upfront cost due to their advanced design and electronic controllers, their long-term savings in energy efficiency and maintenance often justify the investment.
Brushed Motors: These motors are cheaper to produce and purchase initially, making them a cost-effective choice for simpler, low-budget projects.
Cost Difference between BLDC Motors and Brushed Motors
6. Control and Precision
BLDC Motors: They offer superior control and precision, thanks to their electronic commutation. This makes them ideal for applications requiring precise speed and position control, such as robotics or electric valves.
Brushed Motors: Their control is less precise, and they are better suited for applications where basic functionality is sufficient.
7. Applications
- Brushed motors are commonly used in scenarios where high performance is not a priority and cost is a key factor. They are well-suited for simple, low-budget applications such as toys, small household appliances, and basic industrial equipment.
- In contrast, BLDC motors are the preferred choice for high-performance applications that demand efficiency, precision, and durability. These include advanced fields like robotics, electric vehicles, drones, and sophisticated industrial machinery, where their superior performance and longer lifespan provide significant advantages.
Applications Difference between BLDC Motors and Brushed Motors
By understanding these differences, you can better evaluate which motor type aligns with your project’s requirements. In the next section, we’ll explore the advantages of BLDC motors in greater detail to help you see why they are often the preferred choice for modern applications.
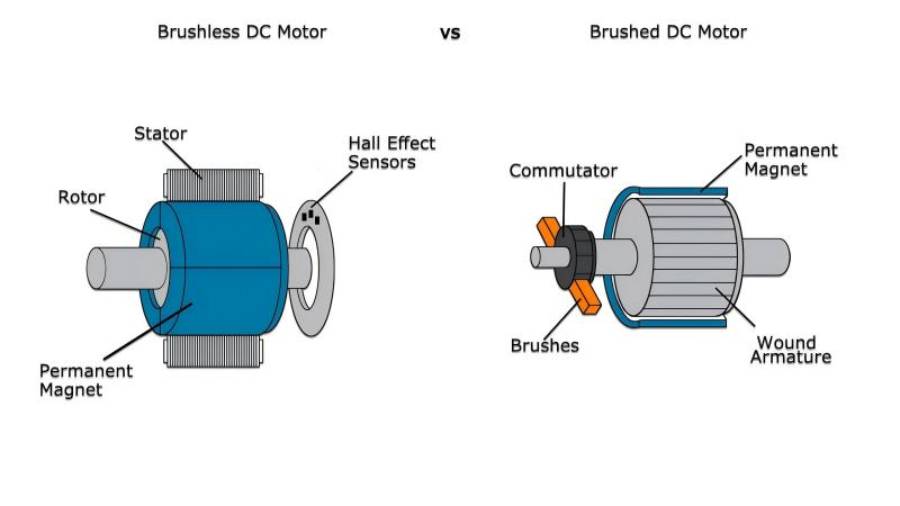
Advantages of BLDC Motors
BLDC motors have become the go-to choice for many modern applications, and for good reason. Their advanced design and performance characteristics offer several advantages that make them stand out compared to traditional brushed motors. Here’s a closer look at why BLDC motors are often the better option:
1. Higher Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of BLDC motors is their energy efficiency. Because they don’t rely on brushes for commutation, there’s no energy loss due to friction. This means BLDC motors can convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into mechanical power, reducing energy consumption and operating costs. For example, in smart home devices like automated blinds or sanitary dispensers, this efficiency translates to longer battery life and lower electricity bills.
2. Longer Lifespan
BLDC motors are built to last. Without brushes that wear out over time, these motors can operate reliably for thousands of hours, even in demanding environments. This makes them ideal for applications where downtime is costly or inconvenient, such as in medical equipment or industrial automation systems.
3. Low Maintenance
Since BLDC motors don’t have brushes that need regular replacement, they require minimal maintenance. This not only reduces long-term costs but also ensures consistent performance over time. For instance, in electric valves or vending machines, where accessibility for maintenance can be challenging, BLDC motors are a practical and hassle-free solution.
4. Quiet and Smooth Operation
BLDC motors operate more quietly and smoothly compared to brushed motors. The absence of brush-commutator contact eliminates the noise and vibration typically associated with brushed motors. This makes BLDC motors perfect for noise-sensitive applications, such as medical devices or home appliances, where a quiet operation is essential.
5. Precise Control
Thanks to their electronic commutation, BLDC motors offer superior control over speed and position. This precision is critical in applications like robotics, where accurate movement is necessary, or in electric valves, where consistent performance is key. The ability to fine-tune motor performance also makes BLDC motors versatile for a wide range of industries.
6. Compact and Lightweight
BLDC motors are often more compact and lightweight than their brushed counterparts, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. For example, in drones or portable medical devices, the smaller size and weight of BLDC motors can significantly enhance performance and usability.
7. Environmentally Friendly
With their higher efficiency and longer lifespan, BLDC motors contribute to reduced energy consumption and waste. This makes them a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious projects, such as renewable energy systems or eco-friendly appliances.
In summary, the advantages of BLDC motors—ranging from higher efficiency and longer lifespan to low maintenance and precise control—make them a superior choice for many modern applications. However, it’s also important to consider the disadvantages of brushed motors to fully understand why BLDC motors are often the preferred option. Let’s explore that in the next section.
Disadvantages of Brushed Motors
While brushed motors have been a reliable choice for decades, they come with several disadvantages that can limit their suitability for modern applications. Understanding these drawbacks is essential when comparing them to more advanced options like BLDC motors. Here’s a closer look at the key disadvantages of brushed motors:
1. Shorter Lifespan
One of the most significant drawbacks of brushed motors is their limited lifespan. The brushes, which are essential for commutation, wear down over time due to constant friction with the commutator. This wear and tear mean that brushed motors often require replacement or repair much sooner than BLDC motors, especially in high-speed or high-load applications.
2. Higher Maintenance
Brushed motors demand regular maintenance to replace worn-out brushes and clean the commutator. This not only increases operational costs but also leads to downtime, which can be particularly problematic in industrial or commercial settings. For example, in a production line or a vending machine, frequent maintenance can disrupt operations and reduce productivity.
3. Lower Efficiency
The friction between the brushes and commutator in brushed motors results in energy loss, making them less efficient compared to BLDC motors. This inefficiency can lead to higher energy consumption and increased operating costs, especially in applications where the motor runs continuously, such as in electric valves or conveyor systems.
4. Noise and Vibration
Brushed motors tend to generate more noise and vibration due to the physical contact between the brushes and commutator. This can be a significant disadvantage in noise-sensitive environments, such as medical facilities or smart home devices, where quiet operation is crucial.
5. Limited Speed and Performance
Brushed motors are generally less capable of handling high-speed or high-performance applications compared to BLDC motors. The mechanical limitations of the brush-commutator system can restrict their speed range and make them less suitable for tasks requiring precise control or rapid adjustments, such as in robotics or advanced automation systems.
6. Heat Generation
The friction and sparking that occur between the brushes and commutator can generate significant heat, which may require additional cooling mechanisms. This heat can also contribute to faster wear and tear, further reducing the motor’s lifespan and efficiency.
7. Environmental Concerns
Brushed motors are less environmentally friendly due to their lower efficiency and shorter lifespan. The frequent replacement of brushes and the higher energy consumption contribute to increased waste and energy use, making them a less sustainable option compared to BLDC motors.
When Are Brushed Motors Still Useful?
Despite these disadvantages, brushed motors still have their place in certain scenarios. They are often chosen for low-cost, low-complexity applications where performance and efficiency are not critical. For example, in simple household appliances, basic toys, or small DIY projects, the affordability and simplicity of brushed motors can make them a practical choice.
In summary, while brushed motors have been a reliable workhorse for many years, their disadvantages—such as shorter lifespan, higher maintenance, and lower efficiency—make them less suitable for modern, high-performance applications. In the next section, we’ll help you decide which motor type is better for your specific needs.
Which Motor is Better for Your Needs?
Choosing between a BLDC motor and a brushed motor ultimately depends on your specific application requirements. Both motor types have their strengths and weaknesses, and understanding these can help you make an informed decision. Here’s a guide to help you determine which motor is better for your needs:
When to Choose a BLDC Motor
BLDC motors are the better choice for applications that demand:
High Efficiency: If energy consumption is a concern, such as in battery-powered devices or smart home systems, BLDC motors are the clear winner. Their brushless design minimizes energy loss, ensuring longer battery life and lower operating costs.
Long Lifespan and Low Maintenance: For applications where reliability and minimal downtime are critical—like medical equipment, industrial automation, or electric valves—BLDC motors are ideal. Their brushless design means fewer wear parts and less maintenance.
Precision and Control: If your project requires precise speed or position control, such as in robotics or advanced vending machines, BLDC motors offer superior performance thanks to their electronic commutation.
Quiet Operation: In noise-sensitive environments, such as medical devices or home appliances, BLDC motors operate more quietly and smoothly compared to brushed motors.
Compact and Lightweight Designs: For applications where space and weight are limited, such as drones or portable devices, BLDC motors provide a compact and lightweight solution.
When to Choose a Brushed Motor
Brushed motors may still be a suitable option for:
Cost-Sensitive Projects: If your budget is tight and performance requirements are modest, brushed motors are a cost-effective choice. They are simpler to manufacture and require less complex control systems.
Low-Complexity Applications: For basic tasks like small household appliances, toys, or DIY projects, brushed motors offer a straightforward and reliable solution.
Short-Term or Prototype Use: If you’re building a prototype or a short-term project where long-term durability isn’t a concern, brushed motors can be a practical and affordable option.
Key Questions to Ask
To determine which motor is better for your needs, consider the following questions:
- What is my budget for the motor and its maintenance?
- How important is energy efficiency in my application?
- Does my project require precise control or high performance?
- Will the motor operate in a noise-sensitive environment?
- How critical is long-term reliability and minimal downtime?
By answering these questions, you can weigh the advantages of BLDC motors against the disadvantages of brushed motors and make the best choice for your project.
In the final section, we’ll summarize the key points and provide a clear call-to-action to help you take the next step.
Conclusion
The debate between BLDC motors and brushed motors is not about which motor is universally better, but rather which one is better suited for your specific needs. BLDC motors, with their advantages such as higher efficiency, longer lifespan, low maintenance, and precise control, are often the preferred choice for modern, high-performance applications like smart home devices, robotics, and medical equipment. On the other hand, brushed motors, despite their disadvantages like shorter lifespan and higher maintenance, remain a cost-effective and practical solution for simpler, low-budget projects.
When making your decision, consider factors such as energy efficiency, maintenance requirements, noise levels, and the complexity of your application. If you’re designing a cutting-edge device that demands reliability and precision, a BLDC motor is likely the best fit. However, if you’re working on a straightforward, cost-sensitive project, a brushed motor might be all you need.
At Etonm Motor, we specialize in providing custom motor solutions tailored to your unique requirements. Whether you need a high-performance BLDC motor for a robotic system or a cost-effective brushed motor for a simple appliance, we’ve got you covered.
Ready to find the perfect motor for your project? Contact us today to explore our range of Planetary Gear Motors, Worm Gear Motors, Flat Gearbox Motors, and more. Let us help you power your innovation with the right motor solution!
Related Reading
- How to Choose the Right BLDC Motor for Robotics Applications
- What is a Planetary Gear Motor?
- What is a Worm Gear Motor? The Ultimate Guide to Its Applications and Benefits
- Top 5 Applications Of BLDC Motors In Industrial Automation
- Brushless DC Motors In Medical Devices | BLDC Motor Applications
- BLDC Motors In Electric Vehicles: Types, Benefits & Applications
- AC Motors Vs DC Motors: Key Differences And Applications Explained